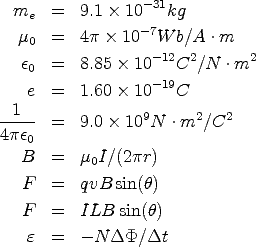
You have 1 hour 30 minutes to answer 7 questions on this exam. Work each problem only on the sheet provided for this problem, using the back if necessary. Please write the name and recitation section on each sheet at the top of the page.
You must indicate the reasoning and show all the steps.
If you are unable to obtain the answer to part of a problem and you need the answer to solve the subsequent parts, use an appropriate symbol for the answer to the previous part and solve in terms of that symbol.
Some useful constants and formulas are given here:
1. (5 points) A charged particle, passing through a certain region of space, has a velocity whose magnitude and direction remain constant. (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is known that the external electric field is zero everywhere, can you conclude that the external magnetic field is also zero? Explain.
2. (5 points) A copper rod is dragged through a uniform magnetic field B with a velocity v as displayed in the following figure. Which end of the rod has a higher electric potential? What happens if the rod is wooden instead? The length of the rod is L.
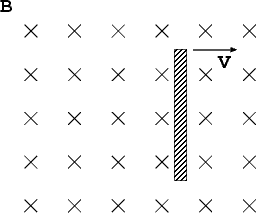
3. (5 points) Deduce the direction of the induced current in the coil when the magnetic
bar is moving closer to the coil (see the following figure). Provide your reasoning.

4. (5 points) The coil of a motor shall burn most probably when the motor is starting up. Why?
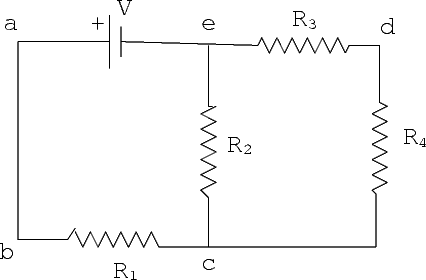
5. (20 points) Consider a multiloop circuit shown in the following figure. The battery has an
emf V = 10V and all the resistors have resistance of R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 1 .
.
6. (20 points) Three very long parallel straight wires are arranged as shown in the figure. Wires A and C carry equal currents of 10A, and B carries a current of 20A, with the current at C pointing into the page while those at A and B point out of the page. AB and AC are perpendicular to each other, i.e., ABC is a right angle triangle with equal sides.

7. (15 points) A charged particle moves through a velocity selector at a constant speed in a straight line. The electric field of the velocity selector is 4 × 103N/C, while the magnetic field is 0.4T.

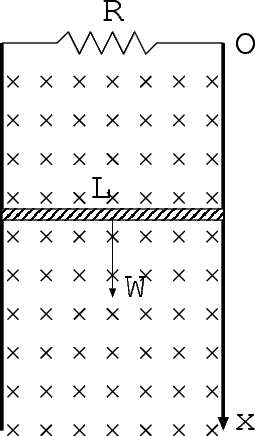
8. (25 points) A conducting rod slides down between two frictionless vertical copper tracks. There
is no kinetic friction between the rod and the tracks, although the rod maintains
electrical contact with the tracks during its fall. A constant magnetic field B = 1T is
directed perpendicular to the motion of the rod. A resistance R = 1 is connected
between the tops of the tracks. The rod has a weight W = mg where m = 0.1kg and
g = 10m/s2 due to gravity. The length of the rod is L = 1m. The rod starts to fall from
the position x0 = 0 from rest and moves in the positive direction of the x-axis.
is connected
between the tops of the tracks. The rod has a weight W = mg where m = 0.1kg and
g = 10m/s2 due to gravity. The length of the rod is L = 1m. The rod starts to fall from
the position x0 = 0 from rest and moves in the positive direction of the x-axis.
 with reference
to vf using the Faraday’s law.
with reference
to vf using the Faraday’s law.